In-Vitro Fertilisation (IVF) in Singapore

Dr Christopher Ng
Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist
MBBS (Imperial College, UK), MMed (O&G) (S’pore), FRANZCOG (Aust-NZ), FAMS (O&G) (S’pore)
In-vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a popular type of assisted reproductive technology (ART) that involves the fertilisation of an egg with a sperm outside the body to form an embryo. The embryo is then transferred into the uterus.
Medically reviewed by Dr Christopher Ng, Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist
What Is IVF?
IVF is the technique in which the egg and sperm are artificially fertilised together outside the woman’s womb in the fertility centre. The fertilised embryos are allowed to grow for a few days before being placed into the uterus.
IVF is the only treatment recommended for women with irreparably damaged or blocked fallopian tubes. It is also suitable for couples with conditions like endometriosis, ovulatory dysfunction, unexplained infertility, failed SOIUI, sperm disorders, and immunological problems.
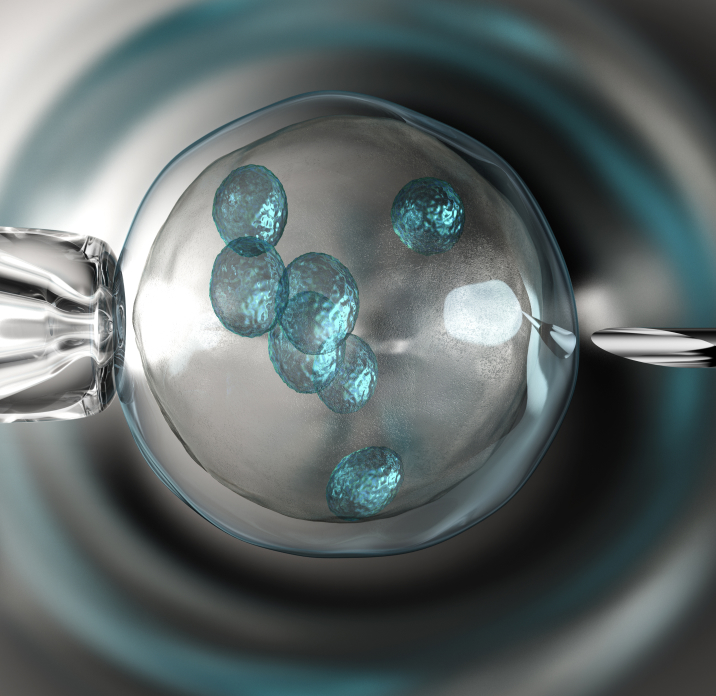
As IVF requires more monitoring than other treatments, couples need to undergo a detailed consultation with our IVF gynaecologist before commencing treatment. Any questions regarding the entire IVF process can be raised at this point. This helps to reduce patient anxiety when they realise that modern IVF treatments are now relatively stress free.
Before the IVF procedure, the couple will need to undergo various blood tests and health screenings for infectious diseases, semen analysis, ovarian reserve evaluation and nutritional advice.


Who Is a Suitable Candidate for IVF Treatment?
Couples seeking IVF will first undergo a detailed medical evaluation to assess their reproductive health and identify any underlying causes of infertility. The IVF doctor will then determine if they are suitable for the procedure.
IVF is usually recommended to couples experiencing infertility caused by:
- Endometriosis
- Tubal factor infertility, such as damaged or obstructed fallopian tubes
- Low ovarian reserve
- Low sperm count and motility
- Ovulation dysfunctions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Unexplained infertility
How to Prepare for IVF
The success of IVF depends on the patient’s overall health, the quality of the embryos and the skill of the IVF doctor. After the couple is deemed eligible for IVF, the doctor will recommend several preparatory measures. These include eating a well balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight, eliminating smoking and alcohol consumption and taking prenatal supplements.
Step-by-Step Process of the IVF Procedure
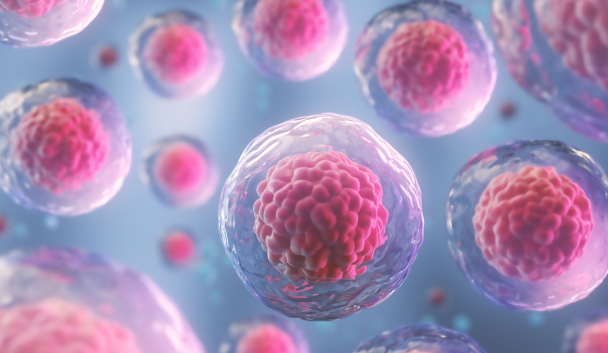
IVF Stage 1: Ovarian Stimulation
To increase the number of eggs, daily fertility hormonal injections are given for a 10- to 12-day period to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple mature eggs during a stimulated cycle. Patients usually administer these injections at home. Ultrasound scans and blood tests are done every few days to assess the growth of the eggs. The dose of the hormones injected may be adjusted accordingly to ensure optimal growth of the eggs.
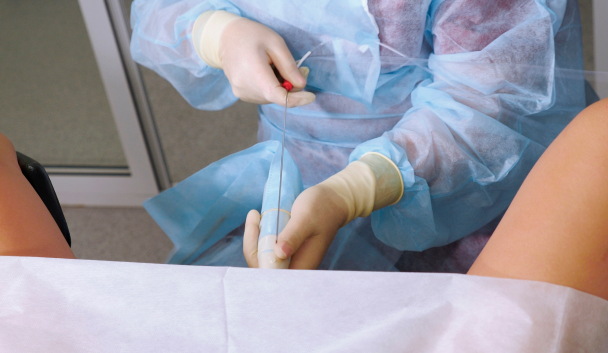
IVF Stage 2: Egg Collection
Eggs of the desired size are collected trans-vaginally using a special needle attached to an ultrasound probe. The patient will be sedated during the retrieval process to minimise any discomfort.
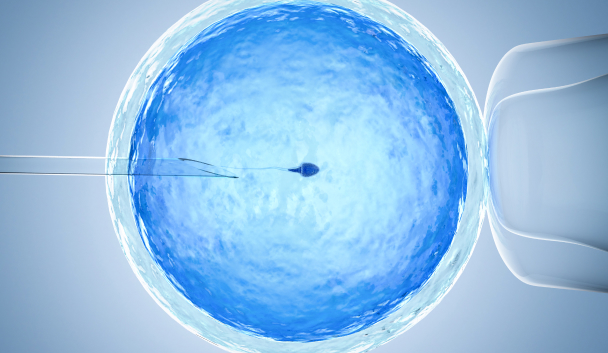
IVF Stage 3: Fertilisation
At the time of the egg collection, the husband will have to produce a fresh semen sample. He is advised to abstain from sexual intercourse for three days beforehand to improve sperm quality. The best-quality sperms are selected and prepared for insemination (fertilisation). Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is used to increase the number of successfully fertilised embryos available for embryo transfer and involves injecting a single sperm into each egg via a microneedle.
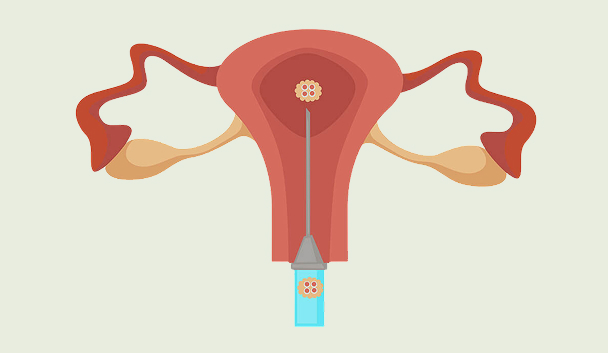
IVF Stage 4: Embryo Transfer
The embryologist will carefully monitor the growth of the embryos for the next few days and select the most suitable ones for embryo transfer. A maximum of two embryos can be transferred into the uterus using a fine catheter. Any extra good-quality embryos will be frozen and stored for future use.
The patient will be given daily hormonal support to maintain the lining of the uterus (endometrium) and to enhance the chances of the embryos implanting. A pregnancy test is then performed 14 to 17 days after embryo transfer at our IVF clinic.
The pregnancy rates for IVF-ICSI treatments at our IVF clinic vary according to various factors such as the patient’s age (woman in particular), the quality of eggs and sperms, the duration of infertility and the general state of health of the couple, among the other male and female infertility factors. Generally, women below the age of 35 have a higher chance of conceiving.
What Are the Risks Associated with IVF Treatment?
While IVF is a safe and established procedure, there are still some risks to take note of. These include:
Multiple Pregnancies
When more than one embryo is transferred to the uterus, there is an increased risk of multiple pregnancies (e.g. twins, triplets).
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
This occurs when too many ovarian follicles are stimulated in response to the fertility injections, leading to the ovaries swelling and the accumulation of excessive fluid into the abdomen.
Complications During Egg Retrieval
Complications during egg retrieval are unlikely but may include bleeding, infection, and damage to the bowels or bladder.


What Are the Side Effects of IVF Treatment?
The fertility drugs taken during IVF treatment can cause temporary side effects, including:
- Breast tenderness due to high oestrogen levels
- Mild bloating, cramping and constipation
- Nausea or vomiting
- Hot flashes or night sweats
- Light vaginal spotting or bleeding
- Bruising from IVF injections
What to Expect After the IVF Procedure
Patients may experience light vaginal bleeding or spotting in the first few days after embryo transfer. The IVF doctor will prescribe hormonal supplements, such as progesterone, to support the uterine lining and improve the chances of implantation.
About 14–17 days after the embryo transfer, the patient will return to the IVF clinic for a pregnancy blood test which is more sensitive and accurate than a urine test. It measures the level of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in the patient’s bloodstream (which is a hormone secreted by the placenta during pregnancy).
If the test results are positive for pregnancy, the mother will be managed by the obstetrician until her successful delivery. If IVF is unsuccessful, the gynaecologist may recommend another IVF cycle, explore alternative fertility treatments or discuss the next steps tailored to the patient’s needs.
Success Rate of IVF Treatments in Singapore
The success rate of IVF treatments varies depending on specific factors, with the main determinant being the woman’s age. Generally, women under 35 years old have a 32% to 55% chance of conceiving through IVF, while women over 40 will have a success rate of only 1% to 10%.
Other factors that may affect the success rate of IVF include:
Egg, Sperm and Embryo Quality
The better the quality of the egg, sperm and embryo, the higher the chances of success.
Medical Conditions
Uterine abnormalities, maternal medical conditions, ovarian dysfunction and poor sperm quality can all affect the chances of a successful outcome.
Lifestyle Factors
Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption and obesity can lower the quality of one’s sperm and eggs, which can affect fertilisation rates, embryo quality and ultimately the success of an IVF cycle.
Increasing One’s Chances of Success with IVF
To optimise one’s chances of success with IVF, doctors recommend that one should maintain a healthy weight, have a balanced diet, exercise regularly, reduce stress, quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption. In addition to these healthy habits, consulting an experienced fertility specialist is important, so that patients can receive appropriate medical advice and care for the best possible outcome.

FAQs about IVF
A single IVF cycle can usually produce multiple embryos, which are sufficient for two to four transfers on average. If the first transfer fails, the remaining embryos can be transferred the next time round. There is no limit to the number of IVF cycles that a couple can undergo, as some couples may require more cycles to achieve pregnancy. Ultimately this would depend on the cost and the couple’s determination to get pregnant.
No, IVF does not increase the risk of birth defects compared to natural conception. Furthermore, IVF in some countries (but not Singapore) include genetic testing, which further ensures a higher chance of normal foetal development.
Sex selection prior to embryo implantation is not allowed in Singapore. However, it may be allowed for certain medical reasons, such as if there is a hereditary, sex-linked chromosomal disorder that is present.
If an IVF cycle is unsuccessful, most fertility specialists advise waiting until a full menstrual cycle has occurred, before attempting another cycle. This waiting period allows the body to recuperate.
The IVF procedure can be uncomfortable in some stages, such as during ovarian stimulation (ovaries enlarge due to the hormone injections needed) and egg retrieval, which may result in some cramping. However, these are temporary and usually manageable.
Infertility Services We Provide
From routine women’s health needs to complex medical issues, our clinic is here to support you.
Call us at 6733 8810 or message us by clicking the button.



Dr Christopher Ng
Consultant Obstetrician & Gynaecologist in Singapore
Qualifications & Credentials
- Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (Imperial College, UK)
- Master of Medicine in Obstetrics and Gynaecology (Singapore)
- Fellow of the Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
- Fellow of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore (Obstetrics & Gynaecology)
Dr Christopher Ng is a dedicated obstetrician and gynaecologist with over three decades of experience. Having been educated and trained in Singapore, the UK and the US, Dr Ng brings with him a wealth of experience and medical knowledge that puts his patient’s wellbeing to the fore.
Dr Ng also complements his practice with aesthetics and has obtained Certificates of Competence in all aesthetic procedures recognised by the Singapore Medical Council Aesthetic Practice Oversight Committee.
With over 30 years of dedicated service in the field of women’s health and rejuvenation, Dr Ng remains steadfast in his commitment to provide compassionate, personalised and effective care to all his patients.
Dr Christopher Ng is a dedicated obstetrician and gynaecologist with over three decades of experience. Having been educated and trained in Singapore, the UK and the US, Dr Ng brings with him a wealth of experience and medical knowledge that puts his patient’s wellbeing to the fore.
Dr Ng also complements his practice with aesthetics and has obtained Certificates of Competence in all aesthetic procedures recognised by the Singapore Medical Council Aesthetic Practice Oversight Committee.
With over 30 years of dedicated service in the field of women’s health and rejuvenation, Dr Ng remains steadfast in his commitment to provide compassionate, personalised and effective care to all his patients.
Phone:+65 6733 8810
Fax:+65 6733 8850
After Office:+65 6535 8833
Email:gynaemd@singnet.com.sg
Mon - Friday:0900h to 1730h
Saturday:0900h to 1300h
Lunch Break:1300h to 1400h
Closed on Public Holiday and Sunday